4.3.30. SphereSlice operator¶
The SphereSlice operator slices a 2D or 3D database with an arbitrary sphere. Plots to which the SphereSlice operator have been applied become 2D surfaces that are coincident with the surface of the slicing sphere. The resulting plots remain in 3D space. You can use the SphereSlice operator to slice objects to judge their deviation from being perfectly spherical. An example of the SphereSlice operator is shown in Figure 4.73.
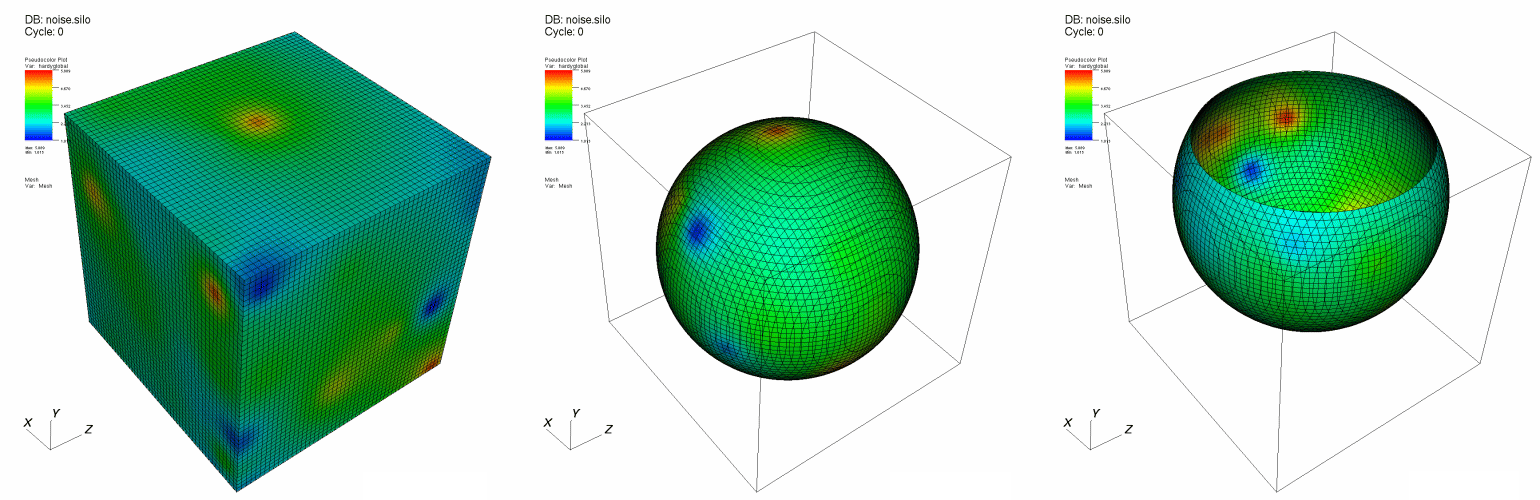
Fig. 4.73 SphereSlice operator example¶
4.3.30.1. Positioning and resizing the slice sphere¶
You can position the slice sphere by setting its origin in the SphereSlice attributes window shown in Figure 4.74 . The slice sphere is specified by a center point and a radius. To change the slice sphere’s center, enter a new point into the Origin text field. The origin is a 3D coordinate that is represented by three space-separated floating point numbers. To resize the sphere, enter a new radius number into the Radius text field.
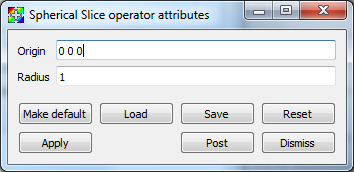
Fig. 4.74 SphereSlice attributes window¶
4.3.30.2. Positioning the slice sphere using the Sphere tool¶
You can also position the slice sphere using VisIt’s interactive sphere tool. The sphere tool, available in the visualization window’s popup menu, allows you to position and resize a slice sphere interactively using the mouse. The sphere tool is an object in the visualization window that can be moved and resized. When the sphere tool is changed, it gives its new slice sphere to the SphereSlice operator. For more information about the sphere tool, read the Interactive Tools chapter.